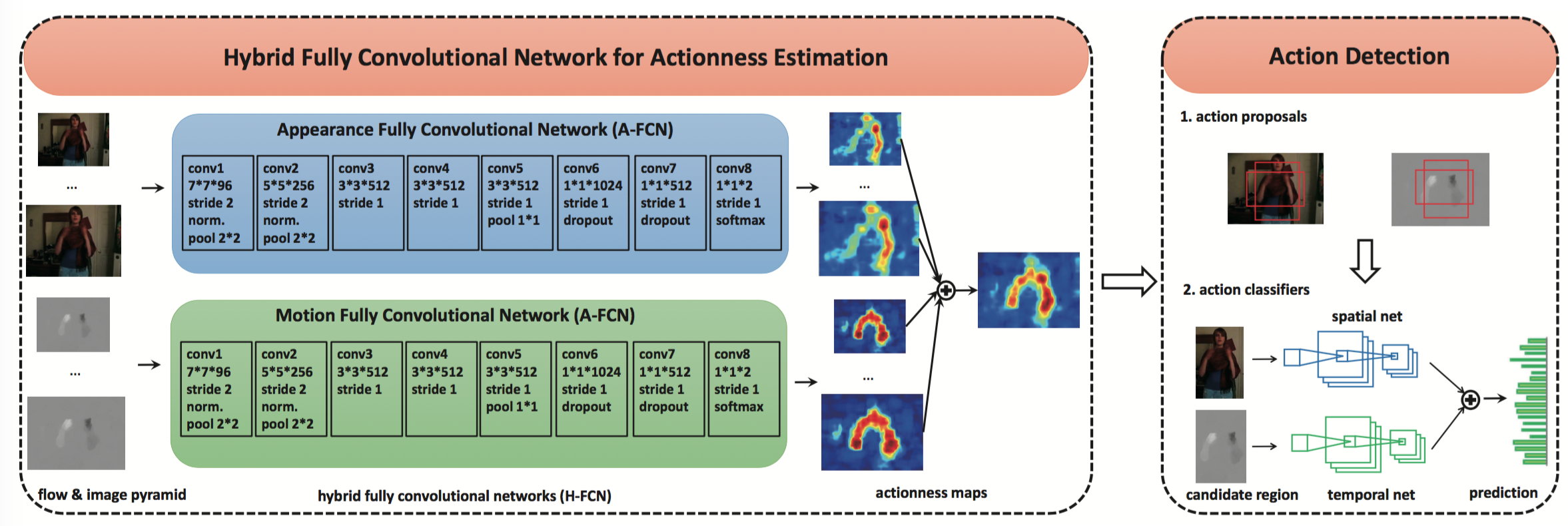
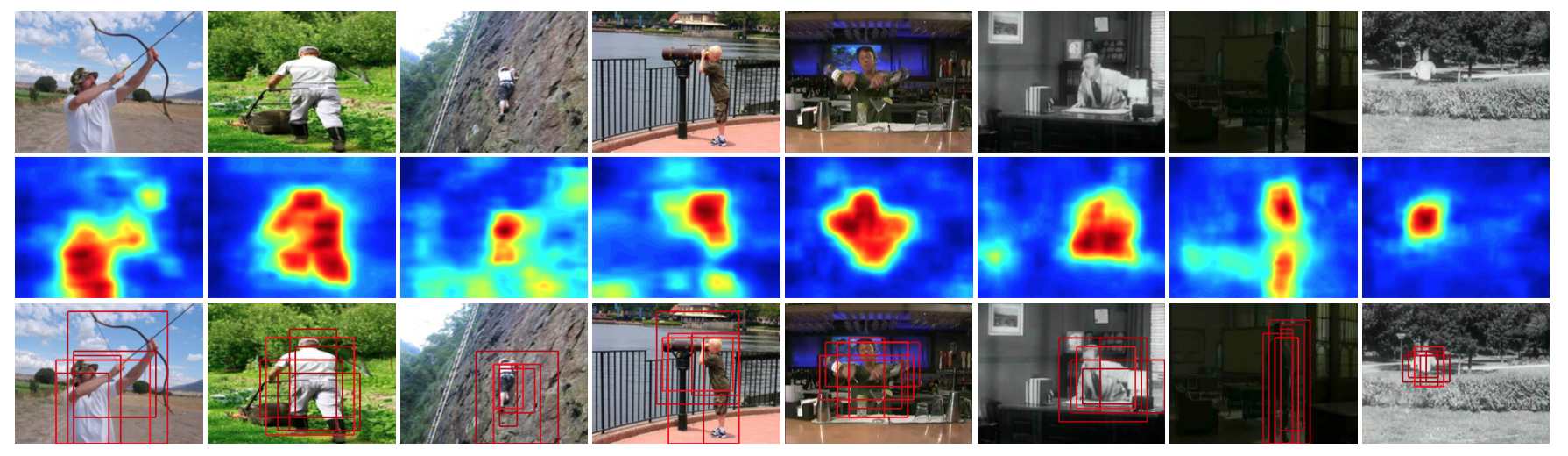
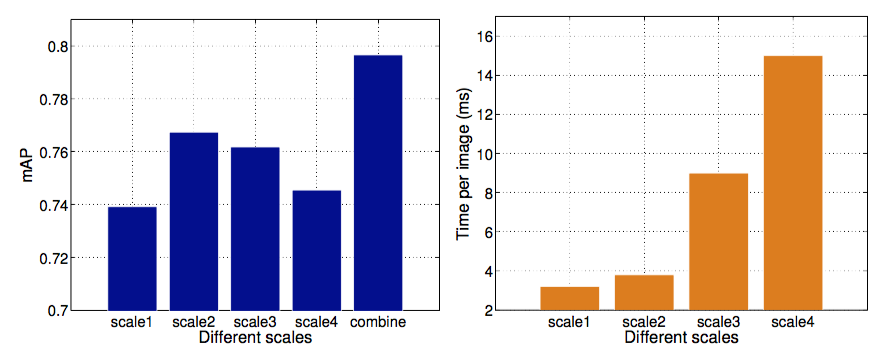
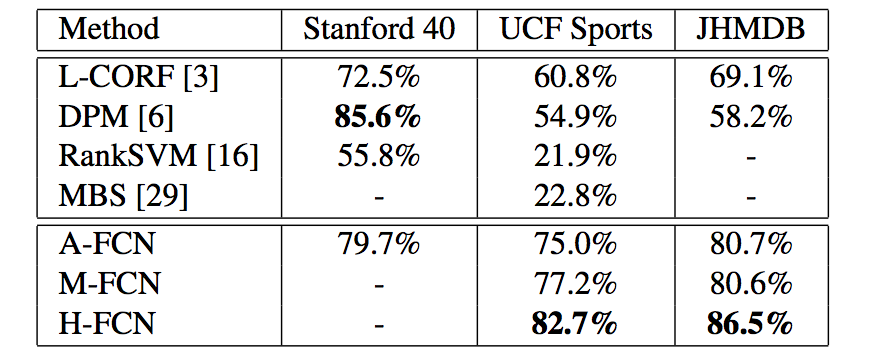
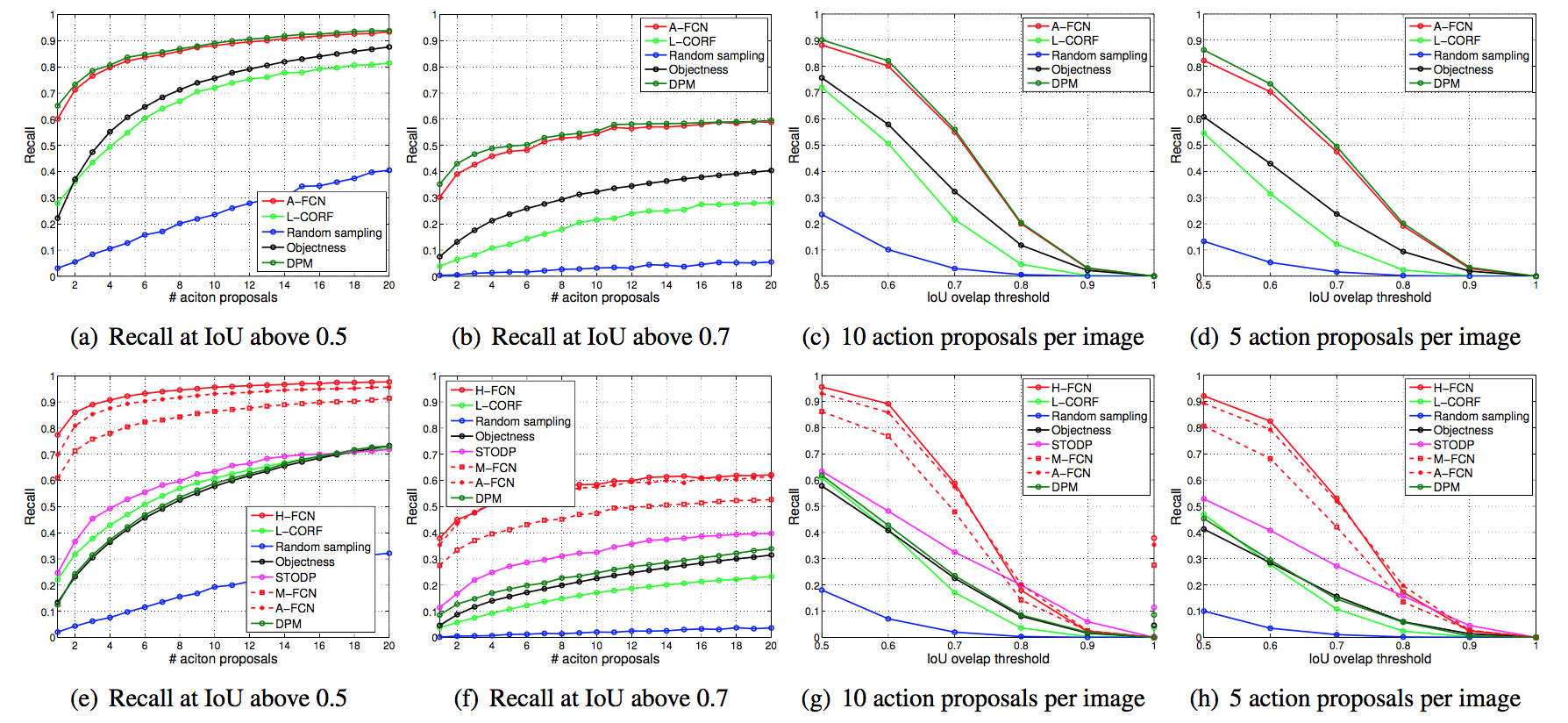
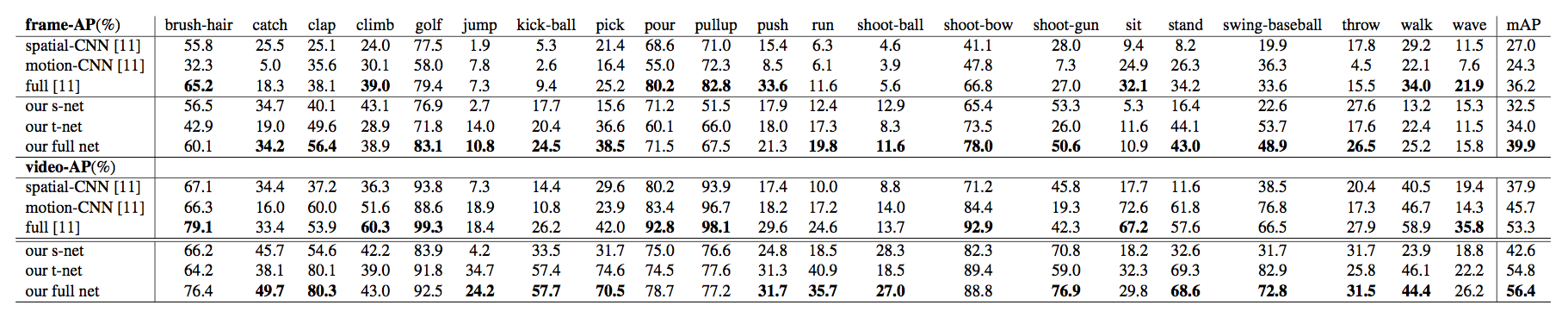
Abstract
Actionness was introduced to quantify the likelihood of containing a generic action instance at a specific location. Accurate and efficient estimation of actionness is important in video analysis and may benefit other relevant tasks such as action recognition and action detection. This paper presents a new deep architecture for actionness estimation, called hybrid fully convolutional network (H-FCN), which is composed of appearance FCN (A-FCN) and motion FCN (M-FCN). These two FCNs leverage the strong capacity of deep models to estimate actionness maps from the perspectives of static appearance and dynamic motion, respectively. In addition, the fully convolutional nature of H-FCN allows it to efficiently process videos with arbitrary sizes. Experiments are conducted on the challenging datasets of Stanford40, UCF Sports, and JHMDB to verify the effectiveness of H-FCN on actionness estimation, which demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to previous ones. Moreover, we apply the estimated actionness maps on action proposal generation and action detection. Our actionness maps advance the current state-of-the-art performance of these tasks substantially.